Cloud Computing Explained: Benefits, Types & Real Use Cases
Modern technology relies heavily on systems that are fast, flexible, and scalable. From streaming movies and storing photos to running business software and analyzing massive datasets, much of today’s digital infrastructure depends on the cloud. That’s why searches for cloud computing explained continue to grow as users and businesses try to understand how this technology actually works.
At its core, cloud computing allows users to access computing resources, such as storage, servers, databases, and applications, over the internet instead of relying on local hardware. Rather than installing software on a single computer or maintaining physical servers, organizations can use cloud services to run applications and store data remotely. This shift has transformed how technology is built, deployed, and scaled. This article explains cloud computing in a practical, easy-to-understand way. You’ll learn what cloud computing is, how cloud technology works, the difference between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, and why cloud computing benefits are driving adoption across industries. Real-world cloud examples are included to show how cloud computing is already shaping everyday digital experiences.
What Is Cloud Computing?
To truly understand cloud computing, it’s important to focus on the core idea rather than the buzzwords. Cloud computing is a model where computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, and software, are delivered over the internet on demand. Instead of owning and maintaining physical infrastructure, users access these resources remotely through cloud services. The foundation of cloud technology rests on three key concepts: on-demand access, scalability, and shared resources. On-demand access means you can use computing power or storage whenever you need it, without long setup times. Scalability allows resources to increase or decrease based on usage, which is especially valuable for businesses with changing workloads. Shared resources mean that multiple users can securely use the same infrastructure, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Another essential concept is virtualization. Cloud providers use virtualization to divide physical hardware into multiple virtual machines. Each virtual machine operates independently, allowing users to run applications as if they had their own dedicated server. This is what makes cloud computing flexible, cost-effective, and reliable. Cloud computing also follows a pay-as-you-go model. Instead of paying upfront for hardware and licenses, users only pay for what they actually use. This model is a major reason behind the widespread adoption of cloud platforms, as it lowers entry barriers for startups and simplifies budgeting for enterprises, one of the key cloud computing benefits.
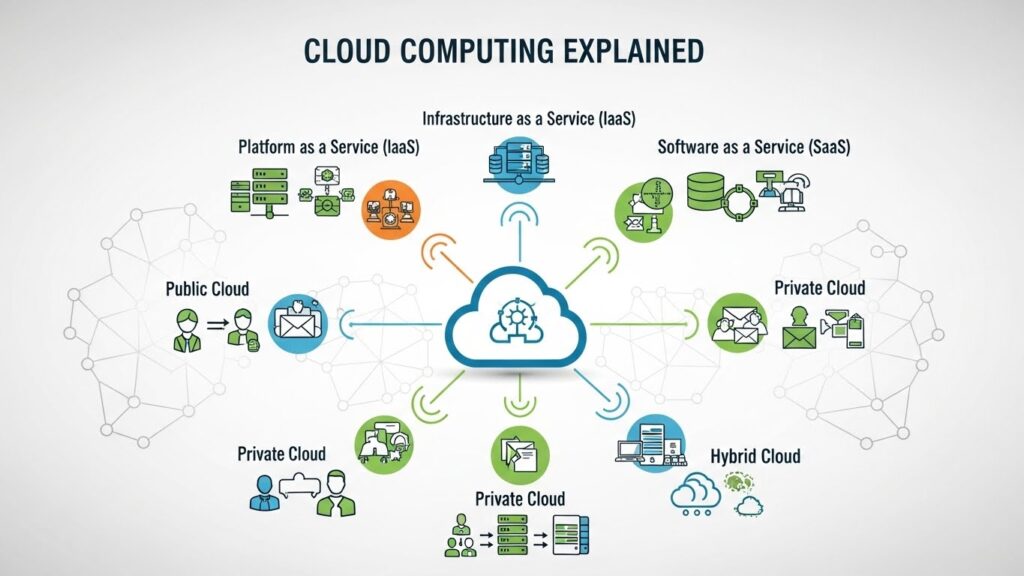
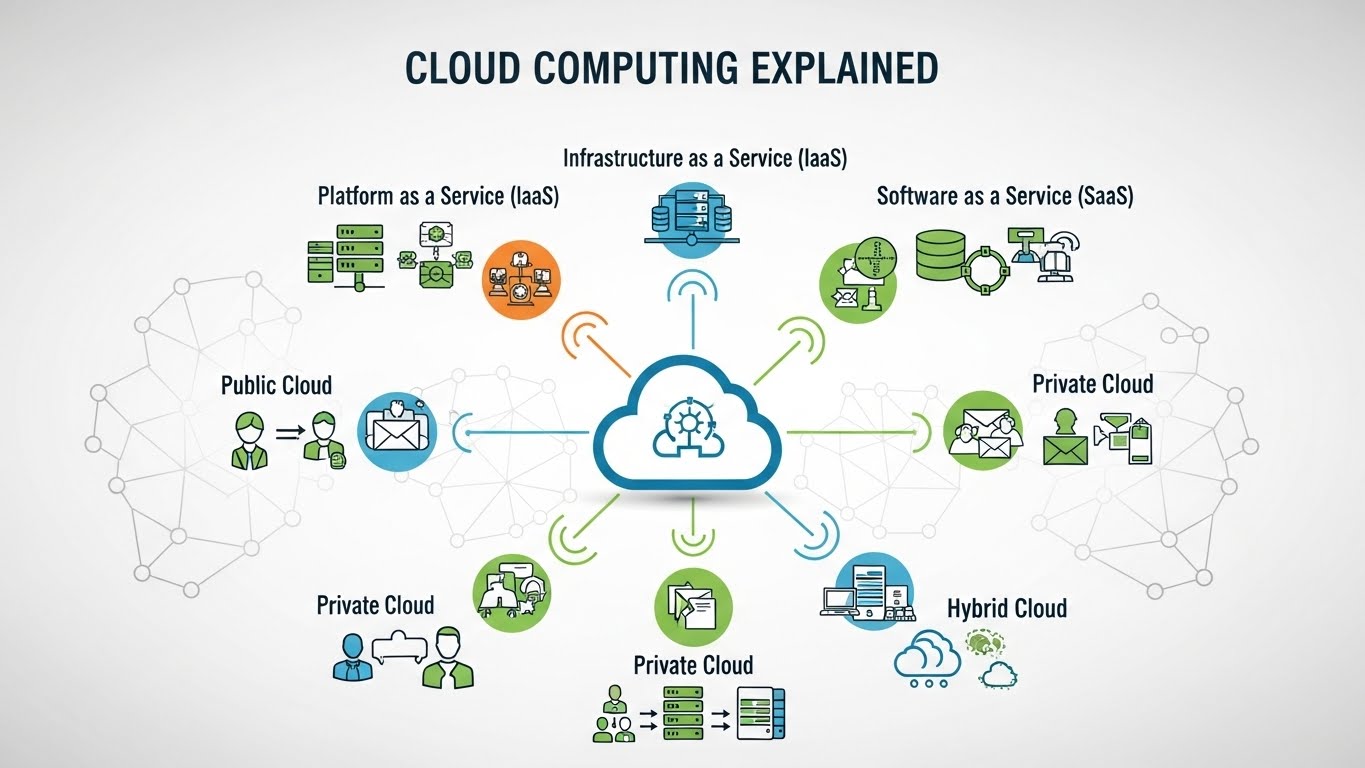
Types of Cloud Computing:
When learning cloud computing, understanding the different cloud deployment models is essential. Not all cloud environments work the same way, and choosing the right type depends on security needs, budget, and control requirements. The three main models are public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud.
Public Cloud
The public cloud is the most common and widely used cloud model. In this setup, cloud resources are owned and managed by third-party providers and delivered over the internet. Users share infrastructure, but their data and applications remain logically separated and secure.
Public cloud platforms are popular because they are cost-effective, highly scalable, and easy to deploy. Businesses and individuals use public cloud services for web hosting, data storage, software applications, and development environments. This model is ideal for startups, small businesses, and organizations that want flexibility without managing hardware.
Private Cloud
A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or managed by a third-party provider, but the infrastructure is not shared with other users. This gives organizations greater control over security, compliance, and performance.
Private clouds are commonly used by enterprises handling sensitive data, such as financial institutions or healthcare organizations. While this model offers stronger customization and control, it typically requires higher costs and more technical management compared to public cloud solutions.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines both public and private cloud environments, allowing data and applications to move between them. This approach gives organizations the flexibility to keep sensitive workloads on a private cloud while using the public cloud for scalability and less critical operations.
Hybrid models are increasingly popular because they balance cost, performance, and security. They allow businesses to scale efficiently while maintaining control over critical systems, one of the practical cloud computing benefits for growing organizations.
Cloud Service Models Cloud Computing Explained:
When people ask for cloud computing explained, they are often trying to understand the different ways cloud services are delivered. These delivery methods are known as cloud service models, and they define how much control users have over software, platforms, and infrastructure. The three main models are SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers complete software applications over the internet. Users don’t need to install, manage, or maintain anything locally; everything runs in the cloud. The provider handles updates, security, and availability, while users simply log in and use the software.
Common cloud examples of SaaS include email platforms, document editing tools, customer relationship management systems, and project management software. SaaS is popular because it’s easy to use, cost-effective, and accessible from any device with an internet connection. This model is ideal for businesses and individuals who want ready-to-use solutions without technical complexity.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a development platform where developers can build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. The cloud provider manages servers, storage, networking, and operating systems, while developers focus purely on writing code.
PaaS is widely used in application development because it speeds up workflows and reduces setup time. It supports collaboration, scalability, and rapid innovation, making it a core component of modern cloud technology. This model is especially valuable for teams creating web and mobile applications.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS offers virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking on a pay-as-you-go basis. Users have full control over operating systems, applications, and configurations, while the provider manages the physical hardware.
IaaS is the most flexible of the three models and is commonly used for hosting websites, running large-scale applications, and managing complex workloads. Organizations that need customization and control often choose IaaS as part of their cloud services strategy.
Conclusion:
Cloud Computing Explained is essential in a world where technology needs to be flexible, scalable, and accessible from anywhere. Cloud computing has fundamentally changed how individuals and businesses use technology, removing the need for heavy hardware, reducing costs, and enabling faster innovation.
From everyday tools like email and file storage to enterprise-level systems running global applications, cloud services are now the backbone of modern digital infrastructure. With different deployment models and service types such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, cloud technology adapts to a wide range of needs. Whether it’s cost efficiency, scalability, or reliability, the cloud computing benefits are driving adoption across every industry. As technology continues to evolve, cloud computing will remain a core foundation for innovation. Knowing how it works, where it’s used, and why it matters helps individuals and organizations make smarter, future-ready technology decisions.
FAQs:
1. What does cloud computing explained mean for beginners?
It means understanding how computing resources like storage, servers, and software are accessed over the internet instead of using local hardware.
2. What are cloud services used for?
Cloud services are used for data storage, software applications, website hosting, development platforms, analytics, and backup solutions.
3. What is the difference between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS?
SaaS provides ready-to-use software, PaaS offers a platform for developers to build applications, and IaaS delivers virtual infrastructure like servers and storage.
4. What are the main benefits of cloud computing?
Key benefits include scalability, cost efficiency, accessibility, reliability, and reduced infrastructure management.
5. Is cloud computing secure?
Yes, major cloud providers use advanced security measures, but users must also follow best practices to protect data and access.
hjhk